Sand Control Screen Pipe for Oil and Gas Wells
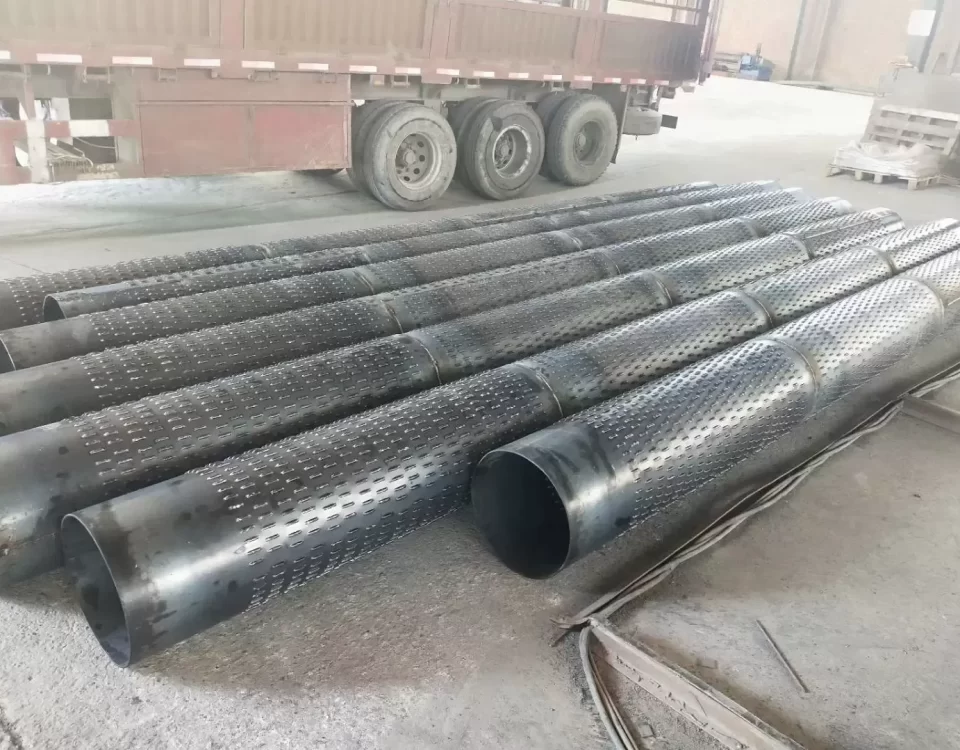
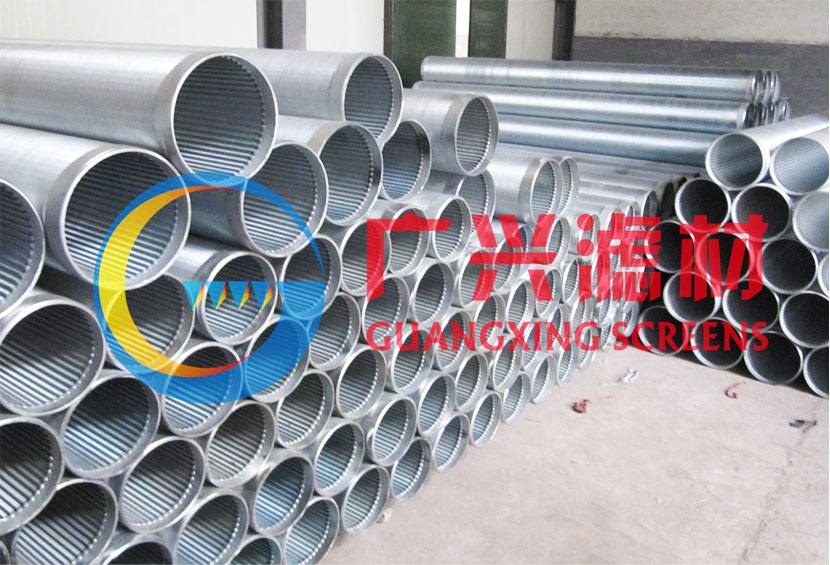
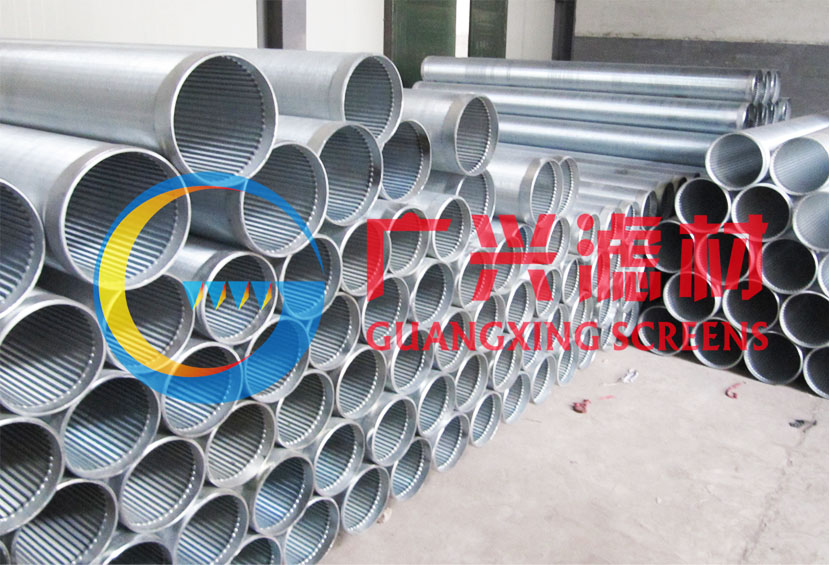
The sand control screen pipe is an essential filtration device deployed in oil and gas wells, as well as water wells, to separate liquids from sand and other particulates. Its primary purpose is sand prevention, a critical factor in maintaining well integrity and productivity. Given the diverse geological conditions and sand layer properties encountered during oil extraction, the screen pipes are available in various types—slotted, perforated, wire-wrapped, bridge-style, and composite—each tailored to specific steel grades and operational requirements.
Product Overview
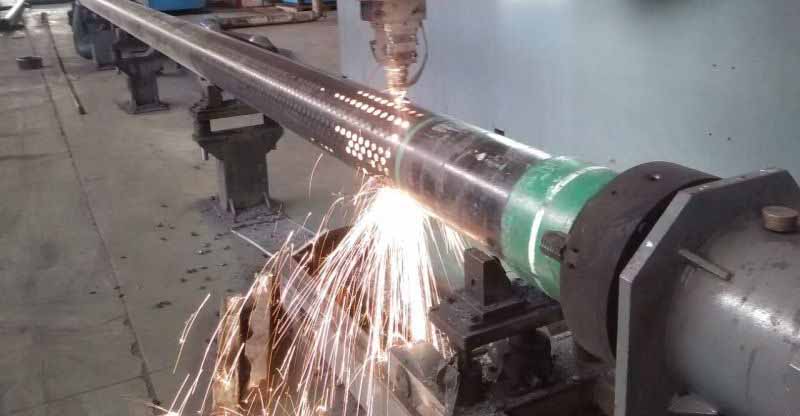
Manufactured to comply with the **API SPEC 5CT** standard, the sand control screen pipe is engineered using the base body of oil casing, ensuring high strength and durability. The design incorporates precise slotting or drilling techniques to create openings that allow fluid flow while blocking sand particles. This product is widely utilized in vertical, deviated, and horizontal wells, offering superior performance in challenging subsurface environments.
Technical Parameters
The sand control screen pipe is available in various configurations to suit different well conditions. Below is a detailed table summarizing its key technical parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Outer Diameter (OD) | Φ114.3 mm to Φ219.08 mm (4.5 inches to 8.625 inches) |
| Wall Thickness (WT) | 5.21 mm to 22.2 mm (0.205 inches to 0.875 inches) |
| Length | Up to 12 meters (customizable) |
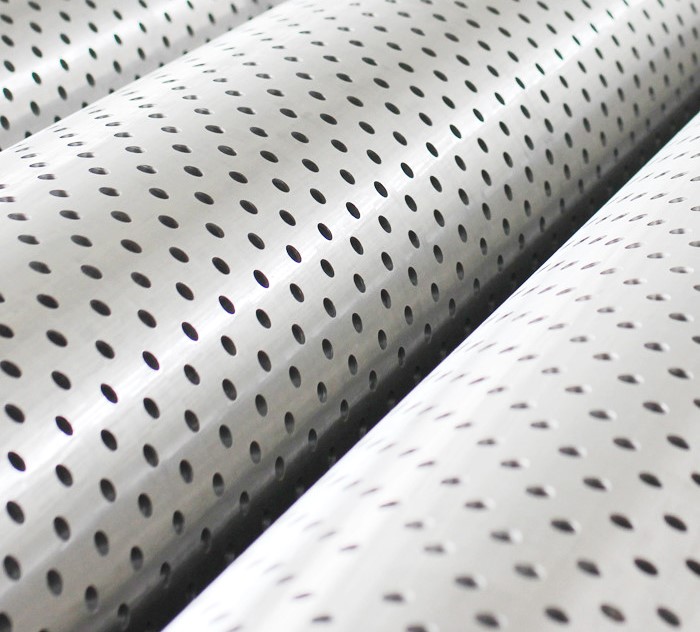
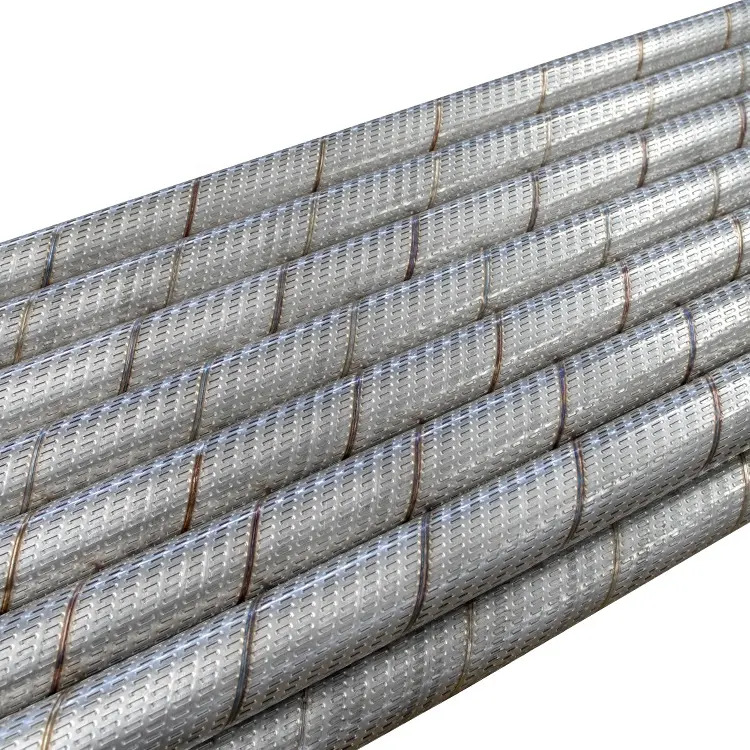
| Slot Width (Slotted Screen) | 0.10 mm to 4 mm (±0.03 mm tolerance) |
| Slot Arrangement | Parallel, staggered, or spiral |
| Number of Slots | Customizable (arbitrary) |
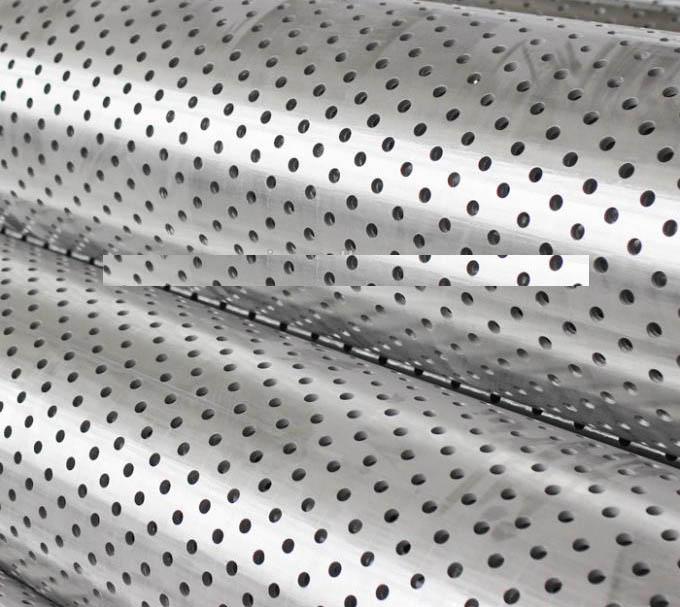
| Hole Diameter (Perforated Screen) | 12 mm to 12.7 mm (±0.1 mm tolerance) |
| Hole Arrangement | Parallel or staggered |
| Materials | Carbon Steel (e.g., J55, N80), Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316L) |
| Surface Treatment | Anti-corrosion coating, galvanization (optional) |
| Open Area | Up to 30% (dependent on slot/hole size and pattern) |
| Operating Pressure | Up to 70 MPa (material and thickness dependent) |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 350°C (material dependent) |
Materials: Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel, such as API grades J55 and N80, is a common material choice for sand control screen pipes due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. It primarily consists of iron and carbon, with small amounts of manganese and other elements to enhance its mechanical properties:
- Tensile Strength: J55 (~517 MPa), N80 (~689 MPa), suitable for high-pressure environments.
- Cost: Economical, ideal for large-scale deployments.
- Surface Treatment: Typically coated or galvanized to mitigate corrosion.
- Limitations: Prone to rust in corrosive environments without protective layers.
Carbon steel screens are widely used in oil and gas wells with moderate corrosion risks. Anti-corrosion treatments, such as epoxy coatings or galvanization, form a protective barrier, extending service life in subsurface conditions.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel, such as grades 304 and 316L, offers enhanced resistance to corrosion and wear, making it ideal for harsh environments. Its composition includes chromium (18-20%) and nickel (8-12%), with 316L featuring molybdenum for added durability:
- Corrosion Resistance: Chromium forms a passive oxide layer, preventing rust.
- Durability: High resistance to pitting and abrasion, especially in 316L.
- Cost: Higher upfront cost, balanced by longevity and reduced maintenance.
- Temperature Tolerance: Suitable for high-temperature wells (up to 350°C).
Stainless steel screens excel in wells with high salinity, sour gas (H₂S), or CO₂ content. The 316L grade, with a PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) of 25-30, is particularly effective in chloride-rich formations, ensuring long-term reliability.
Advantages of Sand Control Screen Pipe
The sand control screen pipe offers numerous benefits, making it a preferred solution in oil and gas operations:
- High Strength and Deformation Resistance: Manufactured from oil casing, it withstands extreme subsurface pressures without deformation.
- Precision Engineering: Smooth, burr-free edges and uniform slots/holes ensure consistent performance.
- Large Flow Area: Open area exceeds that of standard casing, promoting efficient fluid flow.
- Versatility: Suitable for deviated and horizontal wells, with enhanced performance in complex trajectories.
- Corrosion and Wear Resistance: Anti-corrosion coatings create a dense protective layer, extending lifespan.
- Sand Control Efficiency: Effective for sand grains >0.3 mm, reducing equipment wear and blockages.
- Ease of Installation: Large inner diameter and simple design facilitate pipe string configuration.
Scientific Analysis
The sand control screen pipe’s design and performance can be evaluated through fluid dynamics, material science, and structural mechanics. This analysis provides a deeper understanding of its operational efficacy.
Fluid Dynamics and Flow Efficiency
The screen’s slot or hole design optimizes fluid flow while retaining sand. The flow rate through the screen can be modeled using Darcy’s Law for porous media:
Q = -kA (ΔP / μL)
Where:
-
- Q = Flow rate
- k = Permeability of the screen
- A = Cross-sectional area
- ΔP = Pressure difference
- μ = Fluid viscosity
- L = Thickness of the screen
The large open area (up to 30%) increases k, reducing resistance and allowing higher Q. Compared to standard casing, the screen’s flow capacity is 2-3 times greater, minimizing pressure drops. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) studies show that staggered slot patterns reduce turbulence by 15-20%, enhancing flow stability in high-velocity conditions.
For perforated screens, the larger hole size (12-12.7 mm) accommodates higher flow rates but is less effective for fine sand control, making slotted screens (0.10-4 mm) preferable in finer formations.
Material Science: Carbon Steel vs. Stainless Steel
Carbon steel grades like N80 offer a yield strength of ~552 MPa, sufficient for most well depths. However, in wet CO₂ or H₂S environments, corrosion rates can reach 0.2 mm/year without coatings. Epoxy or phenolic coatings reduce this to <0.05 mm/year, adding 5-10 years to service life in neutral pH conditions.
Stainless steel 316L, with a yield strength of ~290 MPa but superior corrosion resistance, maintains integrity in sour wells. Its passive oxide layer (1-3 nm thick) reforms rapidly, reducing corrosion to <0.01 mm/year even in 3% NaCl solutions at 100°C. This makes it ideal for offshore or high-temperature reservoirs.
Structural Mechanics: Strength and Stability
The screen’s casing-based construction enhances its collapse resistance. Finite element analysis (FEA) indicates collapse pressures of 30-70 MPa for N80 carbon steel (depending on wall thickness), while stainless steel 316L withstands 25-50 MPa. The uniform slot/hole distribution minimizes stress concentrations, with a safety factor of 1.5-2 under typical loads.
In deviated wells, the screen resists bending stresses up to 300 kN/m, aided by its high verticality and smooth edges, which prevent crack initiation during installation or operation.
Sand Retention and Wear Analysis
The screen retains sand grains >0.3 mm with >90% efficiency, as tested in formations with D50 (median grain size) of 0.5-1 mm. The smooth, burr-free slots reduce abrasion by 25% compared to rough-cut screens, extending lifespan. In high-sand environments, stainless steel outperforms carbon steel due to its hardness (200-250 HV vs. 150-180 HV), reducing wear rates by 30-40%.
Lifecycle and Cost-Benefit Analysis
In a typical oil well (pH 5-7, 50-150°C), carbon steel screens last 5-10 years with coatings, while stainless steel exceeds 15-20 years. The higher initial cost of stainless steel (2-3 times carbon steel) is offset by reduced replacement frequency, yielding a 20-30% lower lifecycle cost in corrosive conditions.
Conclusion
The sand control screen pipe is a robust, versatile solution for oil and gas wells, meeting API SPEC 5CT standards with precision-engineered slots or holes. Available in carbon steel and stainless steel, it offers a balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Its advantages—high flow capacity, sand retention, and ease of use—are grounded in scientific principles, making it indispensable for modern drilling operations.